15.1.2 Proportion of important sites for terrestrial and freshwater biodiversity that are covered by protected areas, by ecosystem type
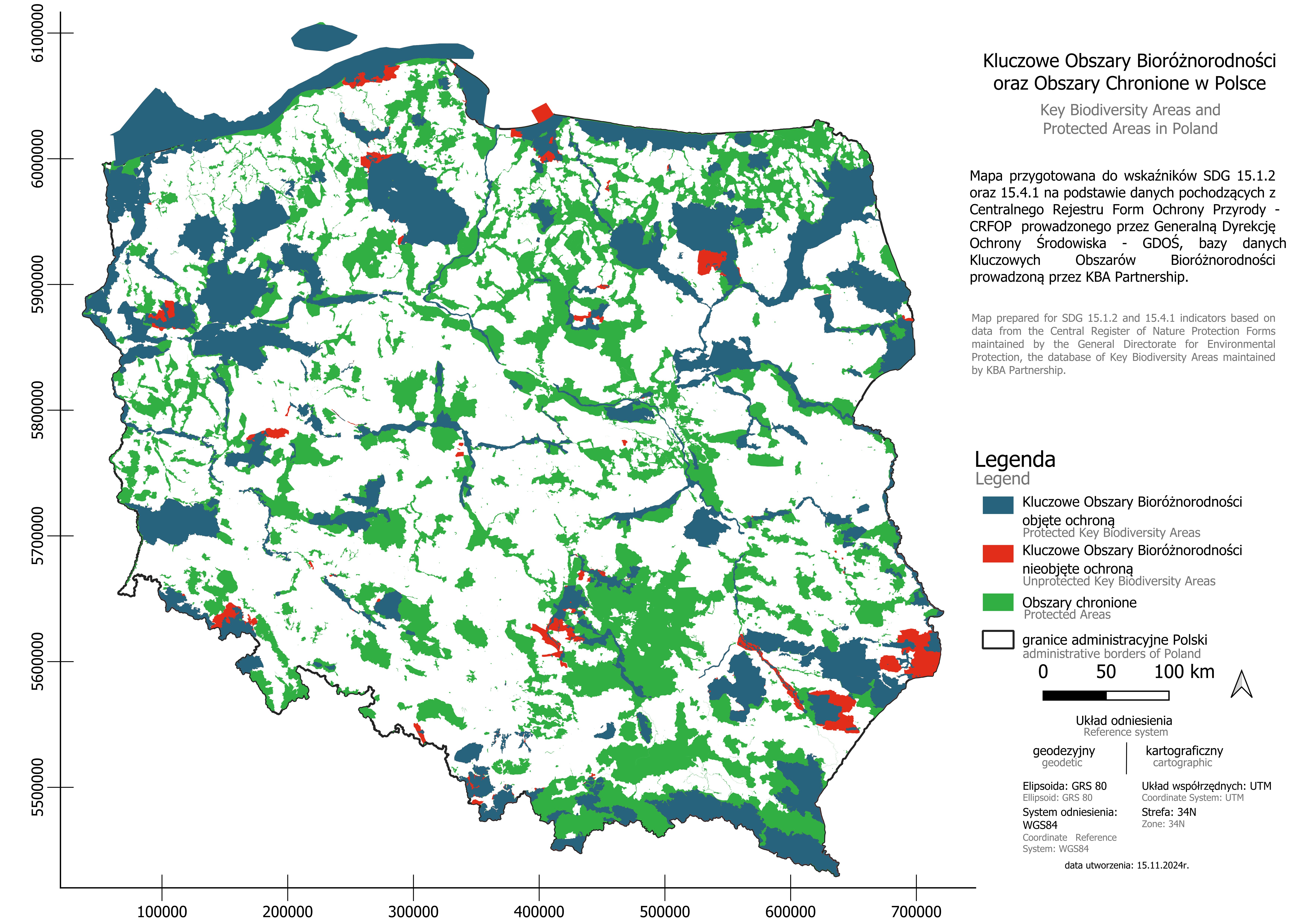
| 15.1.2 The average percentage of Key Biodiversity Areas (KBA) covered by protected areas in Poland (%) | 93.3 |
| 15.1.2a The average percentage of Key Biodiversity Areas (KBA) in freshwaters covered by protected areas in Poland (%) | 98.5 |
| 15.1.2b The average percentage of Key Biodiversity Areas (KBA) on land covered by protected areas in Poland (%) | 92.2 |
| 15.1.2c The average percentage of Key Biodiversity Areas (KBA) in marine waters covered by protected areas in Poland (%) | 97.8 |
Data refer to 2024.
Interpretation
The indicator represents the percentage of areas important for biodiversity that are under protection. It is calculated based on the overlap of protected areas and biodiversity areas. It is expressed as the ratio of the area of protected lands to the total area of lands important for biodiversity within a given ecosystem type.
The higher the value of the indicator, the more effective the protection of biodiversity in individual ecosystems. This, in turn, supports the preservation of ecosystem functions, such as habitat protection, securing natural resources, and providing benefits for people, such as clean air and water.
Here you can find a set of context indicators, the data for which come from official statistics of Statistics Poland. The purpose of context indicators is to complement the results of experimental SDG statistics, deepen information on the monitored phenomena and provide support in assessing progress in implementing sustainable development.
How did we calculate the indicator?
In order to calculate the indicator, the following stages were carried out:
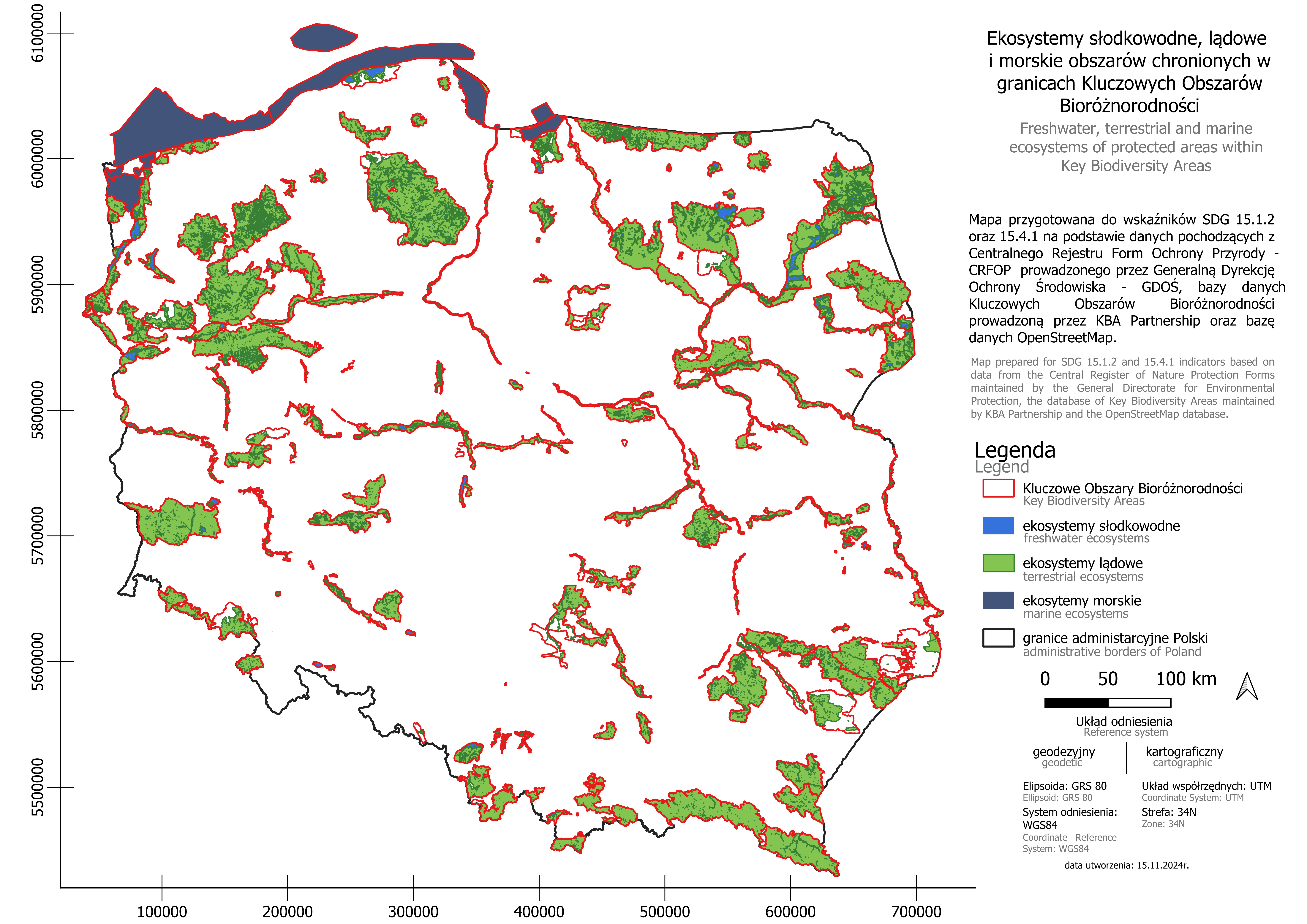
1. Administrative geospatial data from the General Directorate for Environmental Protection (the Central Register of Nature Protection Forms) regarding protected areas in Poland were used, such as national parks, landscape parks, nature reserves, protected landscape areas, Natura 2000 sites ("habitat" and "bird" sites), and RAMSAR areas.
2. Information on Key Biodiversity Areas (KBA) in Poland was obtained from the Key Biodiversity Areas (KBA) Database.
3. Data from OpenStreetMap was used regarding water bodies (lakes, rivers) and wetlands in Poland to distinguish between freshwater and terrestrial ecosystems.
4. Geospatial data were analyzed using QGIS and ArcGIS software to determine the components of each indicator.
5. Based on the overlap of protected areas and biodiversity areas in Poland, indicator 15.1.2 was calculated along with its sub-indicators 15.1.2a and 15.1.2b.
Detailed information on calculations based on the UN methodology can be found in the indicator metadata.
What sources were used to calculate the indicator?
The indicator was calculated based on the methodology proposed by the UN using data from sources:

The Central Register of Nature Protection Forms - a database maintained by the General Directorate for Environmental Protection, which contains detailed information about areas and objects under legal protection in Poland. It serves as the primary tool for collecting and sharing data on nature protection forms, with the goal of supporting conservation efforts and providing access to public information. The register includes various forms of nature protection, in accordance with the Nature Conservation Act.

The Key Biodiversity Areas (KBA) Database - a global database managed by the KBA Partnership that collects detailed information on Key Biodiversity Areas (KBA) worldwide. It contains data on the location, size, and criteria used to designate an area as a KBA. The data from this database are publicly available and are used for both research purposes and the development of environmental policies, as well as for analyzing the impact of development projects on nature.

The OpenStreetMap database is an open, global collection of geospatial data, encompassing detailed information about infrastructure and the environment worldwide. This project collects spatial data, including detailed information about infrastructure elements, administrative divisions, and the natural environment. The data is gathered, updated, and verified by a global community of users and volunteers, ensuring its currency and a high level of detail.
Validation
Being prepared...
What is the meaning of the indicator for sustainable development?
Creating protected areas on land and inland waters is a key tool in preventing the degradation of ecosystems and the loss of biodiversity. It also supports their reconstruction and contributes to climate protection and the maintenance of water resources. Incorporating nature conservation into development policies helps strengthen local economies by supporting tourism, creating jobs and promoting sustainable management of natural resources. Protecting these areas also has a positive impact on the lives of residents, develops infrastructure, increases the investment attractiveness of the region and increases ecological awareness among local communities.

Applications for local government units
Indicator data provides information that can be useful, among others, in spatial planning of regions, identifying areas requiring protection and making decisions in the field of environmental management. Thanks to this information, local government units can manage protected areas more effectively, increasing their tourist and educational values.


